This is the tutorial about how to use OpenRDK together with Player/Stage, in order to have a simulated robot in a 2D world on your own PC.
Installation of Player/Stage
You have two choices: either you use the Player/Stage that comes with your distribution (you can find it, for example, in Ubuntu/Kubuntu distributions), or you download the tarball from the Player/Stage website and use that one. The example explained in this tutorial has been tested with Player/Stage 2.0.3 and 2.0.4.
Now you need to make OpenRDK aware of the presence of Player/Stage. In order to do this, go to src directory and edit the manual.cmake file. You have to set to 1 the variable PLAYER_FOUND and, if you chose to use the SourceForge version of Player/Stage, you need to set to 1 also the following variable: SOURCEFORGE_REPOSITORY_PLAYER.
Now, as every other time that you make changes in manual.cmake file, run:
cmake .and then
makenow the player client module should be compiled and ready to use. We will use a configuration that works as shown in the following figure:
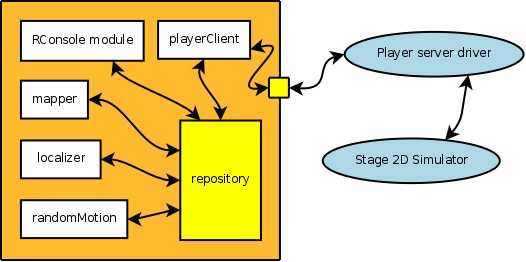
As you can see, the modules of the GUI are in the same agent of the task-related modules. This can be used as a simple solution when you are testing your algorithms. When you want to deploy your application, all you need to do is to remove the GUI modules from the agent. You can create another agent with only the GUI modules and connect with the first one.
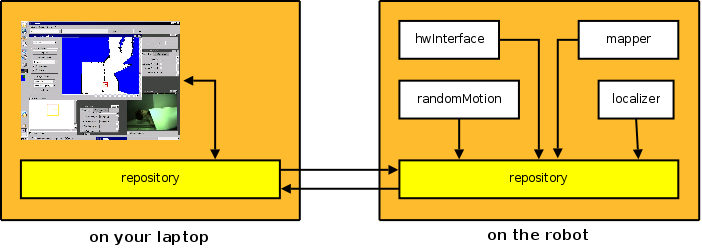
The agent that is running now has inside also some more interesting modules. You can open the robot controller from the "Tools" menu and start moving the robot in the simulated world. If you open the property /mapper/out/map you will see the map created by the module mapper while the robot moves. You can enable the module randomMotion to make it moving randomly around the environment. To enable a module, you can either right-click on the module name, or you can set by hand the property enabled that each module has.